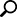- En
- Fr
- عربي
Emotional Intelligence in Leadership and Management
Introduction
Emotional Intelligence is gaining more attention every year throughout the world. Many books have been written on this topic and some of them have been best sellers. A lot of international companies are giving this topic attention and organize courses for their staff on the subject. The United States, Canada, Australia, the Scandinavians and other countries are introducing Emotional Intelligence into their school curriculum because they believe it is important. Emotional Intelligence is based on brain science and most of the books written about Emotional Intelligence are written by scientists. Advances in Emotional Intelligence and Brain Science encourage scientists to continue learning more on the subject. Some people have mentioned that the 21st Century may be known as the century of brain science.
Leadership training in Lebanon has improved and increased in frequency over the last 50 years. Previously leadership training courses emphasized 17 skills and characteristics of a successful leader (none of which are related to Emotional Intelligence). Currently more than sixty different skills are associated with successful leaders. Some of the terms we are using today in our training on leadership and management were not known before, such as: Emotional Intelligence, Emotional Styles, Mindfulness, Focus, and Flow…etc.
This article will introduce:
• the latest in the fields of Emotional Intelligence, Leadership and Management
•some of the concepts and competencies that may be relevant to the Lebanese situation
•ideas that are essential to the military, political, social, and management fields.
The Latest in Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence is defined as: the ability to monitor one’s own and others’ feelings and emotions, to discriminate among them and to use this information to guide one’s thinking and actions[1].
Travis Bradberry and Jane Greaves, in their book Leadership 2.0, defined emotional intelligence as “the ability to recognize and understand emotions in yourself and others, and your ability to use this awareness to manage your behavior and relationships[2].Research has proven that when it comes to performance and success, Emotional Intelligence (EI) is more important than Intelligence Quotient (IQ) because only 20% of people who have high IQ’s are high performers in real life while 80% of those that have a high Emotional Quotient (EQ) are high performers.
This is true of all professions, including the military. Chade-Meng Tan, the author of Search Inside Yourself[3], mentioned this is true in the US Navy. The leadership specialist Wallace Bachman showed that most US Navy commanders are, “more positive and outgoing, more emotionally expressive and dramatic, warmer and sociable (including smiling more), friendlier, and more democratic, more cooperative, more likable and ‘fun to be with’, more appreciative and trustful, and even gentler than those who are merely average[4].
Travis Bradberry and Jane Greaves in their book Leadership 2.0 describe how emotional intelligence works by saying:
“Here is how it works: everything you see, smell, hear, taste, and touch travel through your body in the form of electrical signals. These signals pass from cell to cell until they reach their ultimate destination in your brain”[5].
The challenges for dealing wisely with our emotions are not easy because:
1. Our brains are genetically designed to give emotions the upper hand.
2. The information we receive from our body and our environment has to pass through both the brain stem and the cerebellum before reaching our rational brain.
3. We have to experience things emotionally before we can analyze them rationally.
4. The rational part of our brain, especially the prefrontal cortex (usually referred to as the command center of the brain), cannot stop the effect of emotions but if we are well trained we can deal with the emotions, delay their effect and direct them in a positive rational way. The interaction between the rational and emotional brain is the physical source for emotional intelligence. It is important to emphasize that with training this interaction can be developed in a positive way to increase emotional intelligence.
To better understand emotional intelligence we need to discuss brain science first but before we do that let’s check our information by taking a quick test on information related to brain science.
The following simple self-test will check your information about brain science and perhaps add to what you already know. Correct answers are based on the averages. Please answer True (T) or False (F)
1- The brain of modern humans is exactly the same as primitive human beings.
2- Men are less able to focus on more than one thing at a time than women are.
3- The right side of the brain controls motor skills of the left side of the body.
4- The brains of men and women are exactly the same.
5- Every part of the body is connected to a specific spot in the brain.
6- Men have more connections between the left and right sides of the brain than women do.
7- The number of knowledge cells (neuron cells) in the human brain is more than the total population on earth.
8- The mind and the brain are the same thing.
9- If we get upset it is our fault not the fault of the person or event that upset us.
10- Brain cells regenerate often just as skin cells do.
(Correct answers are at the end of the article.)
Now let’s take a quick look at the human brain.
The above are simple diagrams of the brain. The human brain is a very complex organ, and our information about this organ is still limited and not very much understood by scientists. In fact, we know much more about outer space than we know about the human brain. After the development of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) research of the brain has increased and improved.
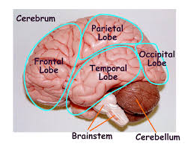
To simplify understanding emotional intelligence let’s consider only three main divisions of the brain: stem, cerebellum and the rest (everything above brainstem and cerebellum in the diagram above) which is usually referred to as the rational brain.
Brain Stem: Is in charge of all involuntary actions of the body including respiration, heart rate, circulation of blood, digestion, etc.
Cerebellum (emotional brain): This is where all emotions are experienced.
The Rational Brain: This area consists of four lobes – frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital).
Through our five senses we detect information that is carried to the brain through the nervous system. It arrives first in the brain stem where it is filtered and then is sent to the cerebellum before it is analyzed by the rational brain.
After the brain receives information it reacts in one of two ways. The reaction of the emotional brain is referred to as the bottom up mind and the reaction of the rational brain is referred to as the top down mind. It is worth mentioning that when the term brain is used we are referring to the organ inside our skull and when we refer to mind we are speaking of the brain in action.
Characteristics of the bottom-up mind and the top-down mind
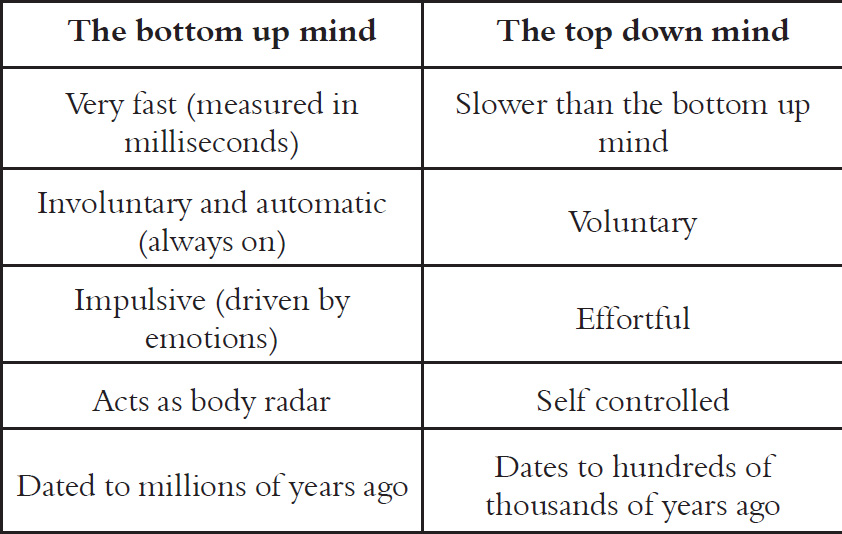
Because the bottom up mind is characterized by automatic quick reactions it often impacts behavior before the rational mind can analyze and respond in a rational way. Emotionally intelligent people are able to have their top down mind in control instead of reacting to the directions given by their bottom up mind. This can be achieved through emotional intelligence skills that can be learned and applied in real life situations. Examples of some skills that may help are: mindfulness, breathing skills, stress management skills, etc. These skills can be taught through training courses and will help people to build and increase their emotional intelligence.
The following facts about the brain will further explain how these exercises will help improve our emotional intelligence:
•The brain learns through patterning
•The brain needs predictability
•The brain seeks meaning
•The brain needs repetition
•The brain needs rehearsing
•The brain learns through feedback
•The brain is social
•The brain has the characteristic of neuroplasticity (Neuroplasticity means that the brain is flexible and able to learn, adapt and improve.)
It has been my experience that trainees attending my courses on emotional intelligence become aware of positive changes in themselves that occur as an outcome of the training they receive. They have reported to me that others around them have commented on and confirmed these positive changes. This verifies that emotional intelligence can be improved by training and is consistent with what brain science has shown.
The six foundation skills of Emotional Intelligence with their characteristics are:
•Self Awareness (know yourself)
o is quiet
o takes his time
o is calm
o is self confident
o is aware of emotional state and consequences of actions related to each
o is in control of emotions
o works continuously to improve self understanding
•Social Awareness (know others)
o is a good listener
o understands feelings of others easily
o has outstanding relations with everybody
o makes others feel comfortable
o understands body language
o listens to others opinions before expressing his own
o can put himself in the position of others
o respects others opinions
•Self Management (lead yourself)
o controls his emotions and directs them in a positive way
o acts wisely, especially during crisis/stress
o is flexible
o thinks before speaking
o accepts himself as he is
o works constantly to increase his self awareness
•Relationship Management (lead others)
o deals positively with others
o is in control during sensitive situations
o is patient
o is a good communicator
o is polite and respectful
o others feel comfortable dealing with him
•Motivate Yourself
o encourages self
o coaches self
o makes full use of time
o rewards self after doing well
o sets high standards for self
o evaluates self performance continuously
o develops skills to the utmost
o strives for excellence
•Motivate Others
o encourages team work
o helps create a positive atmosphere at work
o sets clear objectives and job descriptions
o maintains regular face to face meetings with staff
In order to improve your emotional intelligence score you need to work on developing the above six skills.
Research has shown that physical health and emotional health are connected. So, any stresses in our lives will impact our health. Stress can cause hypertension, heart disease, ulcers, headaches, depression and impacts cancer and diabetes. There are many emotional intelligence skills that can help us relieve stress. Some of these skills are: breathing exercises, progressive relaxation, biofeedback, thought stopping, mindfulness, physical exercise, etc.
Emotional Intelligence in Practice
The following are two simple examples of how emotional intelligence can help in the practice of stress management and problem solving.
Stress Management
People driving on the roads in Lebanon are faced with rude drivers every day. When caught in traffic or waiting in line people cut in, push to be first and seem very inconsiderate of other drivers. When this happens the person being cut off will often experience increased stress, anger and feel their blood pressure rising. If we apply the stress management theory (EAR) which states that for stress to occur:
E – an event occurs
A – appraisal of the event takes place in our rational brain and according to our appraisal we
R – respond to the event
This means that we are to blame for our responses. If we apply this to the man in traffic the “Event” is the behavior of the rude driver. Our “Appraisal” is that the driver has broken the law and deserves to be punished. Our “Response” is anger and stress. This is because, we see him as an enemy and we mobilize ourselves and prepare ourselves for a “fight or flight” situation. Our heart will beat faster and pump blood into our muscles (to meet the fight or flight situation) and as a result our blood pressure will go up. If our appraisal of the event had been positive instead of negative, allowing that he may have had a valid reason to cut us off, it would break the stress cycle.
In summary, it is our mind that is giving orders to our brain and the man cutting us off had nothing to do with the order we sent to our brain. So we are to be blamed if we get upset and we should not put the blame on the other person.
Problem Solving
This folktale may be familiar to you. An old Bedouin who had three children wrote in his will that after his death the camels he owned were to be inherited by his children as follows:
the eldest son was to receive half of the camels
his second son would take one fourth of the camels
and his third son would inherit one sixth of the camels
Upon his death there were eleven camels to be inherited. The three children met but could not divide the camels according to their father’s will because no matter what distribution they considered a fraction of a camel remained. As a result they decided to request the advice of a wise Bedouin. When the wise man arrived riding on his lame camel and had listened to their story he thought a bit and then told them that he wanted to help and since his lame camel was not needed by him any longer he would add it to the inheritance making twelve camels to be divided between the three sons instead of just their father’s eleven.
He told the eldest one, “Now that there are twelve camels to be inherited, you are entitled to half of them. Choose six for yourself and leave.” And so he did.
He then told the second son, “Your share is one fourth of the total so choose any three camels that remain and leave.” And so he did.
Then he told the third son, “Your share is one sixth of the total so choose two of the three remaining camels and leave.” And so he did.
None of the children chose the lame camel because they preferred the healthy ones. After the three sons left with their camels there was only the lame camel left so the wise Bedouin got onto his old camel and went on his way.
In addition to stress management and problem solving emotional intelligence is useful in most of the adaptive leadership skills. These include: communication, teamwork, conflict management, coaching, mentoring, etc.
Emotional Styles
In the past great emphasis was put on behavioral styles (Keirsey, MBTI, etc) that indicate that there are basic types of behavior. The 8 most common types are:
Introvert - Extrovert
Sensing – Intuition
Thinking – Feeling
Judging – Perceiving
Behavioral tests were frequently used in the past to determine where to place employees, vocational guidance, etc. This is now being criticized because behavioral tests were not proven to be scientific. At present, one dimension of emotional intelligence is “emotional styles”. Since emotional styles are based on science it is considered to be more credible than behavioral styles and is gaining ground in leadership and management application.
The six dimensions of Emotional Styles as stated by Richard J. Davidson and Sharon Begley are[6]:
•Resilience: how slowly or quickly you recover from adversity.
•Outlook: how long you are able to sustain positive emotion.
•Social Intuition: how adept you are at picking up social signals from the people around you.
•Self Awareness: how well you perceive bodily feelings that reflect emotions.
•Sensitivity to Context: how good you are at regulating your emotional responses to take into account the context you find yourself in.
•Attention: how sharp and clear your focus is.
Scientists have done studies of the brain and identified specific areas in the brain that control the above styles. They have found that with various techniques and training people have been able to improve their emotional styles and increase their emotional intelligence scores.
For example, in a training course on emotional intelligence the trainer will give exercises that help trainees discover their emotional styles scores allowing them to realize their strengths and weaknesses and where they might need to improve.
Emotional Intelligence and Flow
In the past few years major companies like Microsoft, Erikson, Toyota and others have realized the importance of “Flow”. These companies are now utilizing Flow in an effort to get the best from their workers and to create better relations with their customers.
Wikipedia has defined “Flow” as the mental state of operation in which a person performing an activity is fully immersed in a feeling of energized focus, full involvement and enjoyment; and defined the “State of Flow” as a condition of heightened focus, productivity and happiness.
Flow, Focus and Research
•Our mind can deal with 126 bits of information/sec. A regular conversation takes 40 bits of information/sec. (only 1/3 of our capacity). Since our mind wants to be active it will lose focus if it is not fully occupied. Through appropriate exercises focus can be improved.
•Focus and Flow help us reach a state where we exert minimal effort to achieve optimal results.
•In flow the brain releases the following chemicals:
o Norepinephrine (helps with focus)
o Endorphins (block pain)
o Anadamide (clear insight)
o Serotonin (bonds people together)
o Dopamine (helps with focus)
(It is important to notice that all of the above chemicals enhance performance and that “flow” is one of the only times these five are produced simultaneously).
Scientists have agreed that the following conditions will enhance flow in management:
o Clear goals
o Immediate feedback
o Challenges that match workers skills
o A sense of control
o Few distractions
o Strong motivation
o Feeling a part of something larger than oneself
o Open communication
o A great deal of trust (among employees and between employee and employer)
o Emotionally Intelligent management and staff
o A work environment that fosters Flow
The story of Green Cargo, a transport company owned by the public sector of one of the Scandinavian countries, is a good example of putting Flow into practice. For 125 years the company was losing money and nobody bothered to do anything about the situation because the government was covering their losses. When new management was put in place and they applied the flow conditions above the company stopped losing money within two years.
The latest in Leadership Competencies
As mentioned earlier, at present, the trainers on leadership are emphasizing in their courses more than 60 competencies. Some of these competencies can be grouped under few main headings or titles. Travis Bradberry and Jean Greaves, in their book Leadership 2.0 (p. 3-11), have grouped the competencies that are critical to performance into 22 skills that go under two main titles: Core Leadership and Adaptive Leadership.
Core Leadership Skills are the basics for successful leadership. They include:
Strategic Skills
•Good vision
•Good judgment
•Good planning
•Courage to lead
Action Skills
•Decision making
•Communication
•Mobilizing others
Results/Achievement Skills
•Risk taking
•Results focus
•Flexibility
Adaptive Leadership Skills include the following and are skills all great leaders have in common:
Emotional Intelligence
•Self- awareness
•Self-management
•Social awareness
•Relationship management
Organizational Justice Skills
•Decision fairness
•Information sharing
•Outcome concern
Character Skills
•Integrity
•Credibility
•Values difference
Development Skills
•Lifelong learning
•Developing others
Leadership in Management
Research has shown that successful organizations have the following characteristics in common:
•Power and decision making being made at all levels of the businesses – not just at the top
•There is true understanding and commitment to achieve the set objectives in all levels of the organization
•The information in these organizations moves between all levels of the organization. It is precise, trusted, and honest thus limiting the chance of gossip, rumors and false information.
•Teamwork and cooperation are expressed at all levels in the organization
•Strategic planning is the basis of all policies and plans of the organization
•Human resources are considered to be the greatest capital of the organization
•Continuous development at the level of the institution and the individual is the main concern of management and staff
•Customer service is made a priority
•Performance Appraisal is consistent and timely
Performance appraisal
It is defined as continuous communication between management and employees in order to achieve objectives both management and employees agreeing upon. These include:
•employee job description
•the level of performance requested from the employee to fulfill his job description
•cooperation of management and employees in fulfilling company objectives
Benefits of Performance Appraisal
A good performance appraisal system will provide the following:
•Better supervision
•Employee motivation
•Enhanced employee production
•Detection of employee weaknesses and ways to improve his skills
•Strengthened relations between the employee and his immediate supervisor
Basic Principals of a Good Performance Appraisal System
•The performance appraisal system is implemented in cooperation with the employee and not imposed upon him
•The planning and implementing of the performance evaluation is a joint effort between management and staff
•The major objective of performance appraisal is to emphasize what the employee has done well rather than pinpointing only mistakes.
Conclusion
Emotional intelligence has proven to be important in education, management, institutional development and for individuals. Countries such as Canada, USA, Australia, and Scandinavia (and others) are making emotional intelligence part of the school curriculum. Major companies are including emotional intelligence in their training of employees. At an individual level, emotionally intelligent people are happier, healthier, better team members, and more content with their lives. Emotional intelligence training may be one way to bring opposing elements together. This is especially important to the Lebanese community with its diverse backgrounds, religions, political groups and people. It is my opinion that emotional intelligence skills should be introduced at all levels and to all people within Lebanon.
Recommendations
To introduce emotional intelligence to any group or institution (including the Army), the following steps should be taken into account:
1.Form a committee to assess the present situation and pinpoint weaknesses and points that needs to be improved. The needs assessment should be done in a scientific way utilizing more than one research tool (questionnaires, interviews, focus groups, etc)
2.Formulate recommendations based on the findings.
3.Set clear objectives for development and the introduction of emotional intelligence skills.
4. Develop a strategic plan with:
a. clear mission, vision and values
b. clear short, medium and long term goals
c. well defined activities
d. clear time table
e. clear evaluation criteria
f. all resources, money and personnel available
5. Implement the plan
6. Evaluate, correct and improve
7. Make annual and semi-annual revisions of the plan. Create action plans to adjust and improve the plan as needed.
8. Repeat the above cycle
Answers to Self-Test about the brain:
1. The brain of modern humans is exactly the same as primitive human beings. False: The brain of modern humans is much more developed than primitive man and is larger in size.
2. Men are less able to focus on more than one thing at a time than women are. True: In general it is more difficult for men to focus on more than one thing at a time than women. Women are capable of cooking, talking on the phone and carrying babies at the same time while men find this difficult.
3. The right side of the brain controls motor skills of the left side of the body. True
4. The brains of men and women are exactly the same. False: they differ in more than one way and this impacts gender differences.
5. Every part of the body is connected to a specific spot in the brain. True
6. Men have more connections between the left and right sides of the brain than women do. False: women on the average have fifty million more connections between the right and left sides of the brain than men do. This improves her communication skills with baby girls often speaking earlier than boys and doing better with verbal communication during elementary school.
7. The number of knowledge cells in the brain is more than the total population on earth. True
8. The mind and the brain are the same thing. False: the mind is the brain in action while the brain is the organ in our head.
9. If we get upset it is our fault not the fault of the person or event that upset us. True
10.Brain cells regenerate often just as skin cells do. False
(If you score 8 out of 10 you are doing well. If your score is below 8 you may want to consider learning more about the subject.)
[1]- Peter Salovey and John D. Mayer, “Emotional Intelligence”, Imagination, Cognition, and Personality 9,no.3 (1990) 185-211
[2]- Travis Bradberry and Jean Greaves, “Leadership 2.0”, (CA Talent Smart 2012)129
[3]- Chade-Meng Tan, “Search Inside Yourself”, (NY HarperCollins 2012)14
[4]- Wallace Bachman, “Nice Guys Finish First”, (NY Pracger, 1988) 133-153
[5]- Travis Bradberry and Jean Greave, “Leadership 2.0”, (CA Talent Smart 2012)129
[6]- Richard J. Davidson and Sharon Begley, “The Emotional Life of Your Brain”,(USA Penguin Group, 2012) xii
الذكاء العاطفي في القيادة والإدارة
يكتسب الذكاء الاجتماعي المزيد من الاهتمام سنويًا حول العالم وقد صدرت الكثير من الكتب حول هذا الموضوع حتى أن بعضها أصبح من الكتب الأكثر مبيعًا. وتعير الكثير من الشركات الدولية أهمية لهذا الموضوع وتقوم بتنظيم دورات لطواقم عملها لتسليط الضوء على هذا الموضوع.
وتعمل الولايات المتحدة وكندا وأستراليا والبلدان الإسكندينافية على إضافة مادة الذكاء العاطفي إلى مناهجها المدرسية لأنها تعتبرها مادة مهمة.
تعتمد مادة الذكاء العاطفي على علم الدماغ ومعظم الكتب الصادرة حول الذكاء العاطفي هي أعمال صادرة عن علماء.
التقدّم في مجال الذكاء العاطفي وعلم الدماغ يشجّع العلماء على مواصلة تعلّم المزيد حول هذا الموضوع وقد ذكر بعض الأشخاص بأن القرن الواحد والعشرين قد يعرف بأنه قرن علم الدماغ.
لقد تحسّن التدريب على القيادة في لبنان وتزايدت وتيرة الاعتماد عليه خلال السنوات الـ 50 الماضية. في الماضي ركزت دورات التدريب على القيادة على 17 مهارة وميزة يجب ان يتمتّع بها القائد الناجح ( لا يرتبط أي منها بالذكاء العاطفي) حاليًا هناك أكثر من 60 ميزة مختلفة مرتبطة بالقادة الناجحين. بعض العبارات التي نستعملها اليوم في دورات التدريب على القيادة والإدارة لم تكن معروفة قبلاً مثل: الذكاء العاطفي، الأساليب العاطفية، التيقظ، التركيز إلخ.
سنعرّفكم من خلال هذا المقال على الأمور التالية:
• آخر الإكتشافات في مجال الذكاء العاطفي والقيادة والإدارة.
• بعض المفاهيم والكفاءات التي قد تكون لها علاقة بالوضع اللبناني.
• أفكار ضرورية في المجالات العسكرية والسياسية والاجتماعية والإدارية.